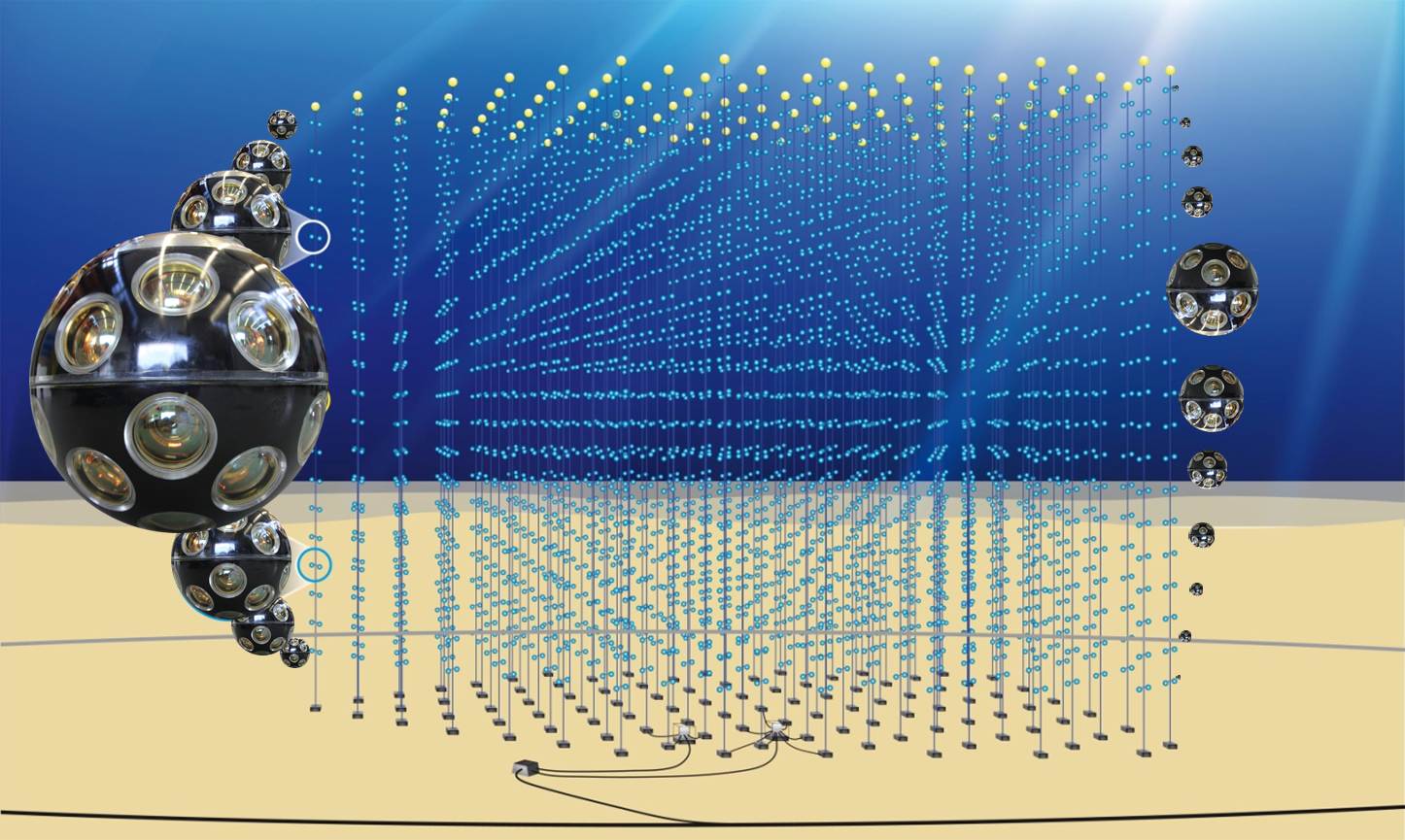
Non-standard interactions (NSIs) in the propagation of neutrinos in matter can lead to significant deviations in neutrino oscillations expected within the standard 3-neutrino framework. These additional interactions would result in an anomalous flux of neutrinos observable at neutrino telescopes. The ANTARES detector and its next-generation successor, KM3NeT, located in the abyss of the Mediterranean Sea, have the potential to measure sub-dominant effects in neutrino oscillations, coming from non-standard neutrino interactions. In this contribution, a likelihood-based search for NSIs with 10 years of atmospheric muon-neutrino data recorded with ANTARES is reported and sensitivity projections for KM3NeT/ORCA, based on realistic detector simulations, are shown. The bounds obtained with ANTARES in the NSI μ – τ sector constitute the most stringent limits up to date.
You may also like
Congratulations to our colleague Yahya Tayalati, awardee of the prestigious Mustafa Prize [Published Oct. 22nd, 2021] The ANTARES Collaboration is proud […]
The size of the coloured sphere is proportionnal to the amount of light received by the optical module (in fact to the […]
The ANTARES detector was the first neutrino telescope in seawater, operating successfully in the Mediterranean Sea for more than a decade and […]
On the 16th April 2013 the ANTARES Instrumentation Line (IL) was successfully connected to the ANTARES seabed infrastructure. This line is very […]