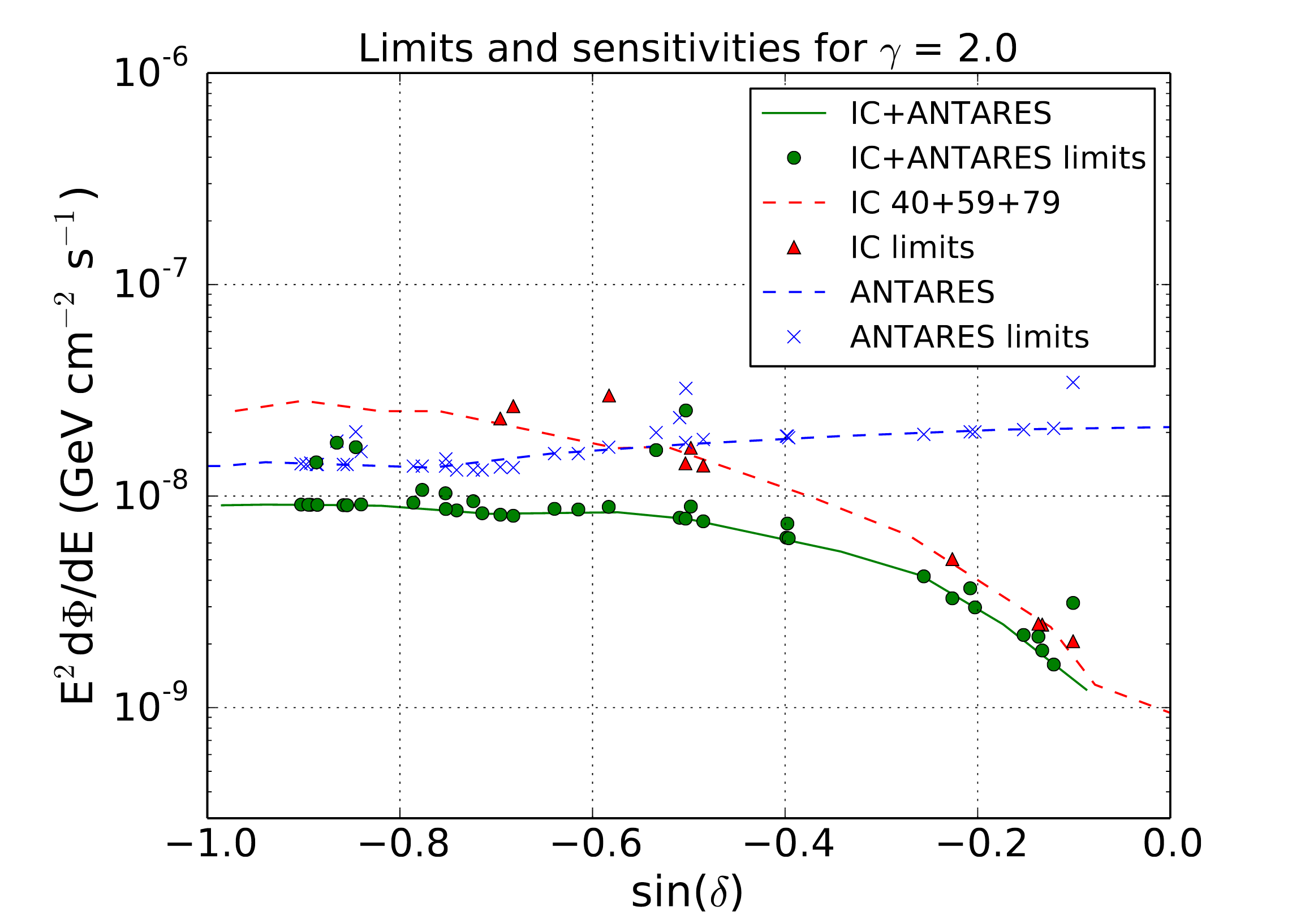
Non-standard interactions (NSIs) in the propagation of neutrinos in matter can lead to significant deviations in neutrino oscillations expected within the standard 3-neutrino framework. These additional interactions would result in an anomalous flux of neutrinos observable at neutrino telescopes. The ANTARES detector and its next-generation successor, KM3NeT, located in the abyss of the Mediterranean Sea, have the potential to measure sub-dominant effects in neutrino oscillations, coming from non-standard neutrino interactions. In this contribution, a likelihood-based search for NSIs with 10 years of atmospheric muon-neutrino data recorded with ANTARES is reported and sensitivity projections for KM3NeT/ORCA, based on realistic detector simulations, are shown. The bounds obtained with ANTARES in the NSI μ – τ sector constitute the most stringent limits up to date.
You may also like
The latest ANTARES results concerning neutrino oscillations were presented this week during the talk given by Tyce de Young, “Latest results from […]
March 2nd, 2006 First line taking data ! After its successful deployment on February 14th, the first Antares line was connected deep […]
The ANTARES and IceCube neutrino telescopes were built with a common objective: the search for sources of astrophysical neutrinos. Although both collaborations […]
On Wednesday Feb. 12th, the KM3NeT collaboration announced the detection of the highest energy neutrino ever detected, dubbed KM3-230213A, of an energy […]