The recently published ANTARES search for a diffuse flux of cosmic neutrinos was highlighted on the AAS Nova site, a feature of AAS journals, on January 31th, 2018. This website is designed to highlight some of the most interesting recent results being published in AAS journals, with the dual intent of gaining broader exposure for our authors, and providing astronomy researchers and enthusiasts with summaries of recent research across a wide range of astronomical fields.
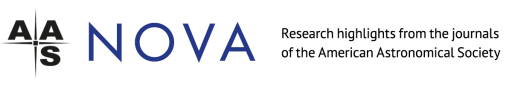
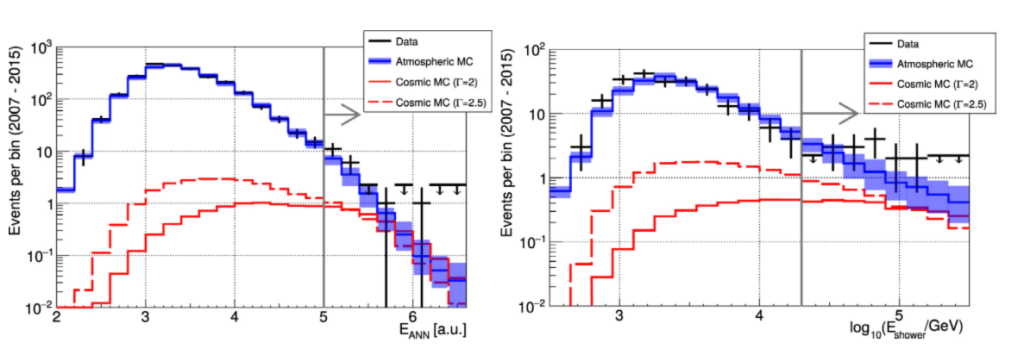
This Highlight presents the results the ANTARES nine-year search for a diffuse cosmic neutrino flux, using both track-like and shower-like events, as shown in the figure below. Over nine years, ANTARES detected a total of 33 events above an energy cutoff of 20 TeV, whereas models predict it should have seen only 24 such events due to atmospheric particles.